How Tesla Builds Its Factories So Quickly
Tesla’s mission is to accelerate the world’s transition to sustainable energy through increasingly affordable electric vehicles and energy products. To ramp production to 500,000 cars per year, Tesla alone will require today’s entire worldwide supply of lithium-ion batteries. The Tesla Gigafactory was born out of necessity and will supply enough batteries to support Tesla’s projected vehicle demand. Today, the Gigafactory produces Model 3 electric motors and battery packs, in addition to Tesla’s energy storage products, Powerwall and Powerpack.
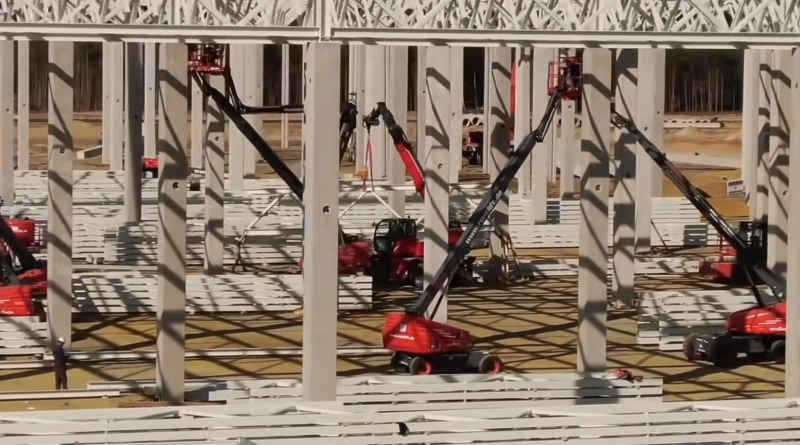
Tesla broke ground on the Gigafactory in June 2014 outside Sparks, Nevada. The name Gigafactory comes from the word ‘Giga,’ the unit of measurement representing “billions.” The Gigafactory is being built in phases so that Tesla can begin manufacturing immediately inside the finished sections and continue to expand thereafter. Already, the current structure has a footprint of more than 1.9 million square feet, which houses approximately 5.3 million square feet of operational space across several floors. Still, the Gigafactory is about 30 percent done. Once complete, Tesla expects the Gigafactory to be the biggest building in the world – and entirely powered by renewable energy sources. Designed to be a net zero energy factory upon completion, the facility will be primarily powered by solar, and installation is already underway.
In mid-2018, battery production at Gigafactory 1 reached an annualized rate of roughly 20 GWh, making it the highest-volume battery plant in the world. Tesla currently produces more batteries in terms of kWh than all other carmakers combined. With the Gigafactory ramping up production, Tesla’s cost of battery cells will significantly decline through economies of scale, innovative manufacturing, reduction of waste, and the simple optimization of locating most manufacturing processes under one roof. By reducing the cost of batteries, Tesla can make products available to more and more people, allowing us to make the biggest possible impact on transitioning the world to sustainable energy.